- ERP Architecture:-
The Most Commonly architectures are:
- Two Tier Architecture
- Three Tier Architecture
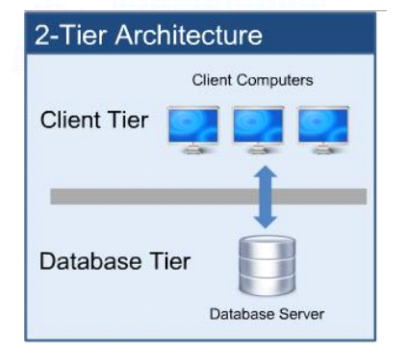
Two tier architecture content two layer client and database. In this architecture as the number of client system increases the load on the database server will increase and the response time will be delayed. due to response time is delayed the output will be very slow on the client system and it is very big disadvantage. To beat this problem we have a new architecture called as three tier architecture.
Advantages:
1.Easy to maintain, modify.
2.Communication Faster.
Disadvantages:
1.Performance Decreases upon increasing the users.
2.Cost-ineffective.
- Three Tier Architecture
Three tier architecture content three layers:
- Database server layer - A server which is responsible only for storing the data is called database server layer.It is central repository of the data. It provides data base services to group of guests or clients.
- Application server layer - A server which is responsible for only executing the application or programs is called application server layer. It receives requests from the presentation layer to take them processed. It also sends back the services to the presentation layer. There are four types of components in application layer.
b.Gateway/Layer: It is a communication protocol of the cross application components such are $, BAPI etc. It provides connection between two SAP systems.
c.Shared Memory: It is a common memory which can be shared by all the work process.
d. Work Process: It's a component to execute the applications.
c.Shared Memory: It is a common memory which can be shared by all the work process.
d. Work Process: It's a component to execute the applications.
- Presentation Server Layer - A server which is responsible. It's an environment or platform where all the users are sent for the services.
Advantages:
1. High performance, flexibility in deployment.
2. Improve data Integrity, Improved client Security.
Disadvantages:
1. Increase Complexity.
2. Increase Efforts.
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a leading provider of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that helps businesses streamline their operations and improve efficiency. In this article, we will explore the architecture of SAP systems, highlighting key components and their functionalities.
Overview of SAP Architecture
SAP architecture refers to the structure and design of SAP systems, which are composed of various layers and components. At the core, we have the SAP application layer, which houses the business logic and processes. This layer interacts with the database layer, responsible for storing and retrieving data. On top of these layers, we find the presentation layer, which enables users to interact with the system through intuitive interfaces. Additionally, SAP systems can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, offering flexibility to suit different business needs.
Key Components of SAP Architecture
a. Application Layer: This layer comprises SAP modules such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Financial Accounting (FI), and Human Capital Management (HCM). Each module contains specific business processes and functions tailored to different organizational requirements.
b. Database Layer: SAP systems rely on robust databases to store and manage vast amounts of business data. Popular database options include SAP HANA, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server. These databases offer high-performance capabilities, ensuring efficient data processing and retrieval.
c. Presentation Layer: The presentation layer is the user interface (UI) through which employees interact with the SAP system. It includes various interfaces like SAP Fiori, Web Dynpro, and classic SAP GUI. These interfaces provide users with access to functionalities, reports, and dashboards.
d. Integration Layer: SAP architecture supports seamless integration with other systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and third-party applications. Integration ensures data consistency, facilitates information exchange, and enables end-to-end process automation.
Benefits of SAP Architecture
Implementing a robust SAP architecture offers numerous benefits for businesses:
a. Streamlined Processes: SAP systems automate and optimize key business processes, reducing manual effort and improving operational efficiency.
b. Data Management: SAP's integrated database layer ensures centralized data management, enabling real-time analytics, reporting, and decision-making.
c. Scalability: SAP architecture accommodates the growth of businesses, allowing for the addition of new modules and functionalities as required.
d. Enhanced User Experience: The intuitive interfaces and personalized dashboards of SAP's presentation layer improve user productivity and satisfaction.













-min.jpg)
0 Comments